The ratio of the effective horizontal stress to the vertical stress is called the coefficient of earth pressure at rest - K0
K0 = Coefficient of lateral earth pressure at rest
1) For coarse grained soils, the coefficient of earth pressure at rest can be estimated by the empirical relationship (Jacky)
2) For over consolidated coarse grained soil, can be modified as ( Mayne and Kulhawy)
OCR = overconsolidated ratio (please check my before blogs)
3) For fine grained, normally consolidated soils Massarsch suggested the following equation for K0,
4) For overconsolidated clays
Example :
Normally consolidated sand phi' = 30, C' = 0, gamma = 18 KN/m^3 determine lateral earth pressure upto 10 m depth (No water table) under rest condition.
K0 = 1 - sin phi' = 1 - sin 30 = 0.5
sigma h' = K0 x sigma v' = 0.5 x (18 x 10) = 90 K Pa
Rankin's Active and Passive states
In the case of at rest condition no wall movement is considered, if the wall movement is considered two things will happen,1) Moving the wall away from soil
2) Moving the wall towards the soil
Rankin's Active State
- Wall movement is away from the soil (towards the excavation)- Initial stress condition is 'at rest condition'
- With wall movement, horizontal stress decreases
- With further wall movement, Mohr circle will touches the failure line (please refer my before blogs) and causing soil failure
- At soil failure, the horizontal stress = sigma a' (active failure stress)
For this situation we need to use Rankin's Active pressure equation,
where,
Sigma a' = Active failure stress
Ka = Coefficient of active earth pressure
Assumptions we need to use this equation,
(1) Ground surface should be horizontal
(2) Back of the wall is smooth (no resistance) and vertical
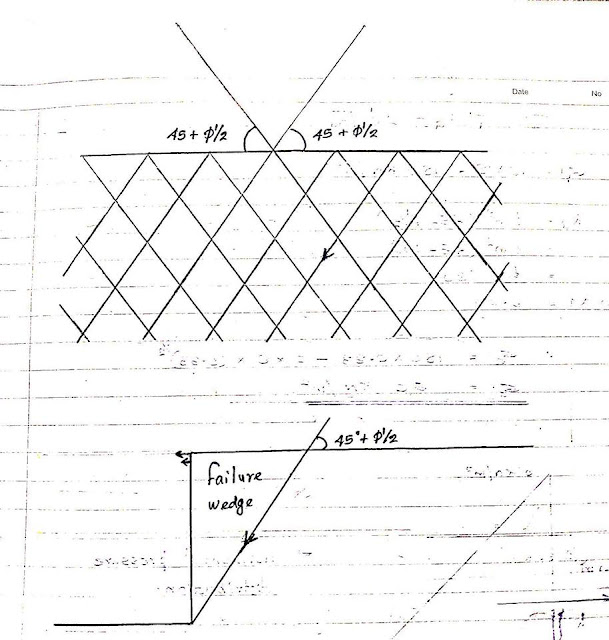
Failure planes
Example :
Determine the active pressure distribution acting on the wall and the total force and it's line of acting.
Ka = tan^2 (45 - 15 )= 0.33
sigma a' = 180 x 0.33 - 2 x 0 x (0.33)^0.5 = 60 KN/m^2
F = 0.5 x 60 x 10 = 300 KN/m
h = 10/3 = 3.3m
Rankin's Passive State
- Wall movement towards the soil (away from the excavation)- Initial stress condition is "at rest" condition
- With wall movement, horizontal stress becomes the major principal stress
- With further wall movement, Mohr circle touches the failure line causing soil failure
- At soil failure, lets assume the horizontal stress to be sigma p' (passive failure stress)
For this situation we need to use Rankin's Passive pressure equation,
where,
Sigma P' = Passive failure stress
KP = Coefficient of Passive earth pressure
Assumptions we need to use this equation,
(1) Ground surface should be horizontal
(2) Back of the wall is smooth (no resistance) and vertical
Failure planes
Example :
Estimate the passive pressure distribution on the wall and determine total passive force on the wall and it's line of action
sigma v' = 10 x 18 = 180 KN/m^2
Kp = tan^2 (45 + 15) = 3
sigma p' = 180 x 3 + 2 x 0 x (3)^0.5 = 540 K Pa
F = 1/2 x 540 x 10 = 2700 KN/m
h = 10/3 = 3.3 m




No comments:
Post a Comment